Installing on CircleCI
Create CircleCI resource classes
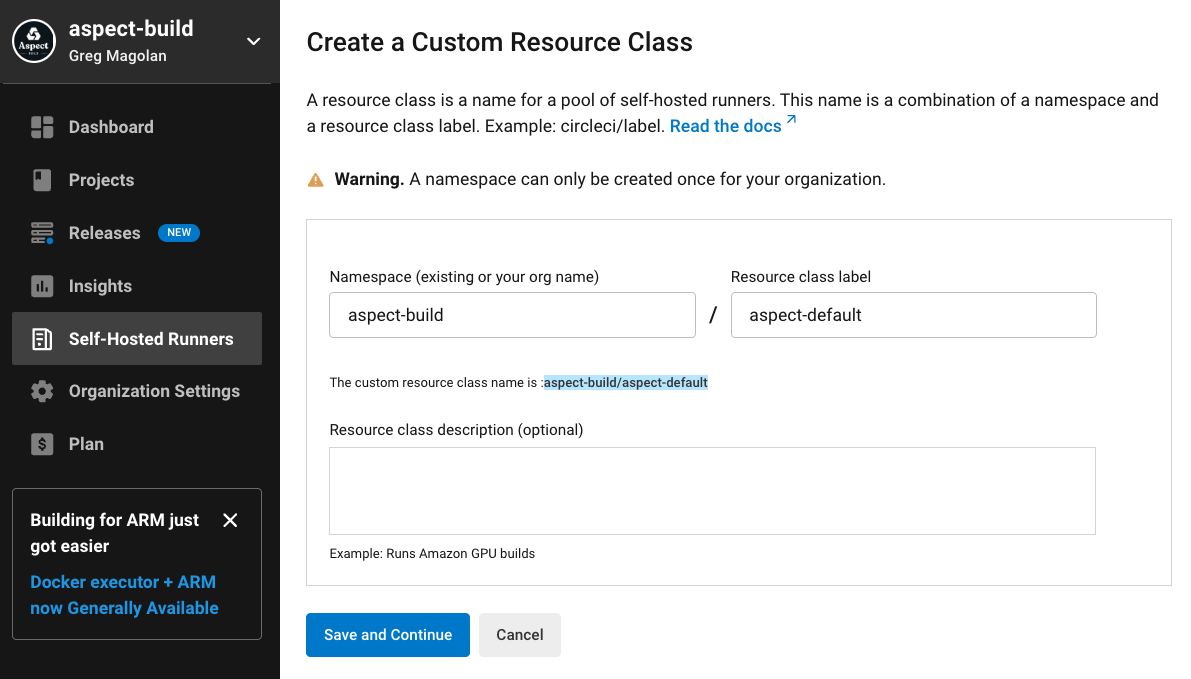
In your CircleCI account, open Self-Hosted Runners.
At least two custom "Resource Classes" are required. Aspect uses these to assign CircleCI jobs to specific runner groups:
- The default runner group resource class is typically
my-org/aspect-default. - The warming runner group resource class is typically
my-org/aspect-warming.
If overriding the queue names in .aspect/workflows/config.yaml, you need to change the resource class names accordingly.
Each additional runner group requires a unique "Resource Class" so that jobs can target it.
CircleCI provides unique tokens for these pools for Aspect-managed self-hosted runners to connect to CircleCI to accept work. Write these down as you'll need them in later steps.
Generate a CircleCI personal access token
In CircleCI, navigate to https://app.circleci.com/settings/user/tokens and generate a New Token.
Aspect recommends creating this token using a bot account so that it is not tied to a human user account.
Provide tokens
For Aspect Workflows to connect to CircleCI, it needs three credentials for each of the two runner pools created above.
resource_classis the Resource Class name created earlier, eithermy-org/aspect-defaultormy-org/aspect-warmingaccess_tokenis the 40-character personal access token created earlier for making API calls to CircleCI.auth_tokenis the 80-character "resource class token" that CircleCI produced when the Resource Class was created.
The resource_class and auth_token are unique per runner pool, but you can re-use the same access_token for each.
There are two secrets to populate with the credentials for the two runner pools. You should format the secret values as a JSON object providing these three keys.
For example:
{"resource_class":"my-org/aspect-default","access_token":"******","auth_token":"******"}
and:
{"resource_class":"my-org/aspect-warming","access_token":"******","auth_token":"******"}
You can set the values in the AWS console:
- Navigate to AWS Console > AWS Secrets Manager > Secrets,
- Locate the keys named
aw_cci_<hash>__<runner pool name>, for example:
aw_cci_63eb73cb0f156210__default and aw_cci_0c03c0e5c34924f0__warming,
and set the "Plaintext" values to the JSON strings for the respective runner pools.
They also appear as separate Key/value pairs in the AWS user interface.
Alternatively, Terraform can supply the value.
An output from the Workflows Terraform module exposes the AWS Secrets Manager Secret ID.
The ID is named runner_secret_ids["runner pool name"] where "runner pool name"
matches the cci_runner_groups input parameter.
For example, if main.tf contains
cci_runner_groups = {
default = {
max_runners = 10
...
}
warming = {
max_runners = 1
...
}
}
Then you configure the secret with:
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "runner" {
secret_id = module.aspect_workflows.runner_secret_ids["default"]
secret_string = "my-secret-for-default"
}
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "runner_warming" {
secret_id = module.aspect_workflows.runner_secret_ids["warming"]
secret_string = "my-secret-for-warming"
}
You should supply the secret_string value using whatever mechanism you already use for managing secrets.
GitHub API token secret
A number of Workflows features require read-only access to the GitHub API. For example, the "Format" task uses a GitHub token to fetch the changed files in a PR.
Create a fine-grained Personal Access Token (PAT) and grant the read permission for Pull Requests,
scoped to any repositories that are tested by Workflows.
You may need to enable the use of PATs in your organization's settings.
Next, copy the token value into Secrets Manager.
- Navigate to Your Cloud Console > Secrets Manager > Secrets,
- Locate the key in the following format
aw_gh_api_token__XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX - Set the value to the fine-grained token GitHub provided.
Alternatively, Terraform can supply the value.
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "gh_api_token" {
secret_id = module.aspect_workflows.github_token_secret_id
secret_string = "my-github-token"
}
Configure the workflow
Now you can update the CircleCI configuration file.
Simple repositories may be able to use Aspect's CircleCI Orb.
Following the instructions in
the Aspect Workflows CircleCI Orb documentation. It is installed into .circleci/config.yaml.
However, CircleCI is limited. The Orb must use the continuations feature, and one workflow can only contain one continuation. As an alternative to using the Orb, you may need a large amount of YAML vendored into the repository.
See https://github.com/aspect-build/aspect-cli/blob/main/.circleci/BUILD.bazel for an example.
A number of Workflows features require read-only access to the GitHub API.
For example, if the "Branch Freshness" strategy is set to rebase, it requires a GitHub token
to make a GET request to https://api.github.com/repos/{owner}/{repo}/pulls/{pull_number}.
Therefore, you must grant a token read permission to Pull Requests,
scoped to any repositories that are tested by Workflows.
Terraform can supply this secret, similarly to the tokens described above.
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "gh_api_token" {
secret_id = module.aspect_workflows.github_token_secret_id
secret_string = "my-github-token"
}